Components of Cardiovascular System
(CVS)
Cardiovascular system is the transport system of the body, through which the nutrients are conveyed to places where these are utilized, and the metabolites (waste products) are conveyed to appropriate places from where these are expelled. The conveying medium is a liquid tissue, the blood, which flows in tubular channels called blood vessels. The circulation is maintained by the central pumping organ called the heart. For Gross anatomy of the CVS, vist : Cardiovascular System: Gross Anatomy
Cardiovascular System
Cardiovascular system is a closed system of tubes made up of the following parts based on their structural and topographical characteristics.
Heart
It is a four-chambered muscular organ which pumps blood to various parts of the body. Each half of the heart has a receiving chamber called atrium, and a pumping chamber called ventricle. For detailed study of human heart, visit: Anatomy of Heart
Heart
Arteries
These are distributing channels which carry blood away from the heart.
- They branch like trees on their way to different parts of the body.
- The large arteries arc rich in elastic tissue, but as branching progresses there is an ever-increasing amount Of smooth muscle in their walls.
- The minute branches which are just visible to naked eye arc called arterioles.
- Angeion is a Greek word, meaning a vessel (blood vessel or lymph vessel). Its word derivatives are angiology, angiography, hemangioma, and thromboangitis obliterans.
Veins
These are draining channels which carry blood from different parts of the body back to the heart.
- Like rivers, the veins arc formed by tributaries.
- The small veins (venules) join together to form, larger veins, which in turn unite to form great veins called venae cavae.
For more details about veins, visit the page: Veins
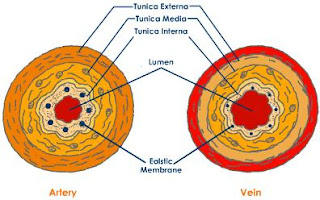
Relative Structure of Artery and Vein
For more details on the difference between arteries and veins, visit the page: Difference Between Arteries and Veins
Capillaries
These are networks of microscopic vessels which connect arterioles with the venules. These come in intimate contact with the tissues for a free exchange of nutrients and metabolites across their walls between the blood and the tissue fluid. The metabolites are partly drained by the capillaries and partly by lymphatics. Capillaries are replaced by sinusoids in certain organs, like liver and spleen.
For more details on capillaries, visit the page: Capillaries
Capillaries
Blood
Blood is a special type of tissue of human body. The character which differentiates it from rest of the tissues of human body is that it is in fluid form. It is composed of Blood Cells and Plasma. Plasma is the watery portion of blood and makes about 55% of the blood volume. The blood cells make about 45% of the blood volume and are of three types:
- Red Blood Cells
- White Blood Cells
- Platelets
Bleeding Finger showing blood
(Source: Southgeist/Wikipedia)






No comments:
Post a Comment
Please do not enter any spam link in the comment box. Thanks